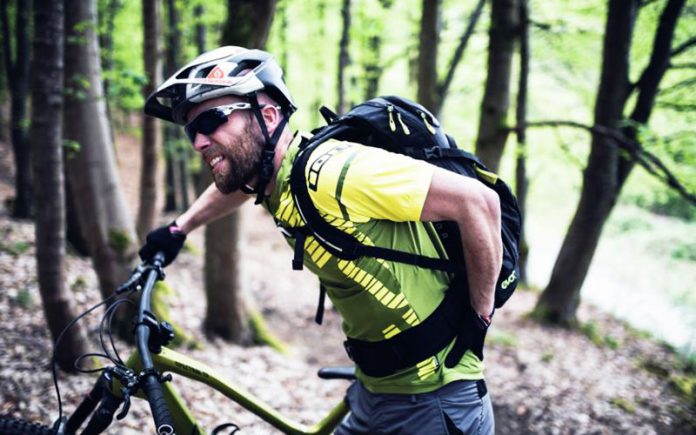
Cycling is one of the most popular and engaging sports with millions around the world engaging in it professionally and for leisure. Just like for every other sport known to man, there are attendant risks involved in cycling. Many people are quick to point to the knees and ankles as vulnerable points for injuries but in reality, it is the lower back that bears the brunt of this physical exertion and not the knees like many are quick to assume. So, the question is, is cycling good for lower back pain?
Research findings have revealed some surprising statistics that shed more light on the extent of injuries suffered by professional cyclists over a certain time period. Of the 116 cyclists surveyed by some Norwegian research scientists, about 94% had suffered one form of injury or another. Only 23% of the total numbers of recorded injuries were actually knee injuries with over 54% of the total number surveyed suffering lower back injuries during the period under review.
Ask many fitness and health experts if cycling is good for the lower back and for the treatment of back injuries and they’ll answer in the affirmative. This is what makes this discovery even more puzzling and brings up some questions begging for answers. Is cycling good for lower back pain? Yes, it is. Are people who engage in cycling regularly prone to back injuries? The answer again is yes. In this article, we will explore the possible reasons why some people suffer lower back pain while cycling and tips for reducing it.
Is Back Pain Caused by Cycling on Road Bikes?
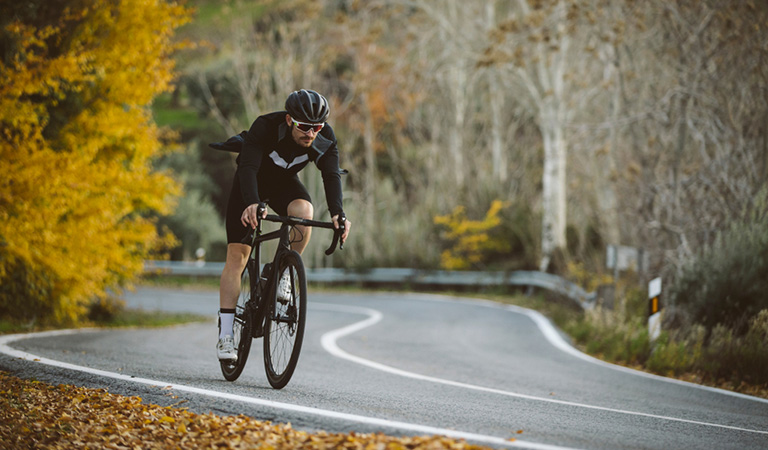

Cyclists may suffer back pain due to muscle fatigue. Constant pedaling leads to exhaustion and hamstrings and calf muscles become fatigued when this happens. This eventually produces muscle pattern changes which eventually affect the back. Riding on road bikes may cause back pain not because these bikes are bad but because of the posture taken by the cyclists when cycling. Below are some possible reasons for this:
Improper bike set-up: Improper bike set-up is one of the root causes of back pains. This may occur;
- When handlebars are too far out
- Cranks are too long
- Unsuitable seat and height position
- When Bike frame is too small
Impaired spinal movement: When a Cyclist has experienced sustain periods of Lumbar flexion, back pain is bound to occur. According to Dr. Shirley A. Sahrmann, Impairments are musculoskeletal pains caused by pressure to the Lumbar spine due to repeated movements and prolonged posture; what this means is that the longer a cyclist maintains a bent forward posture, the most likely he will suffer from back pain.
Wrong back posture: Improper back posture is another cause of back pain for cyclists. Sitting on your bike in a wrong posture for prolonged periods places a lot of stress on your spine which may lead to negative changes and reactions. This could cause problems for your back muscles.
Rough terrain: Cycling in rough terrains increases spine compression. The constant jarring experienced when riding over rough terrains pose physical hazards to cyclists, particularly when riding for long stretches.
Tips on Reducing Low Back Pain for Cyclist
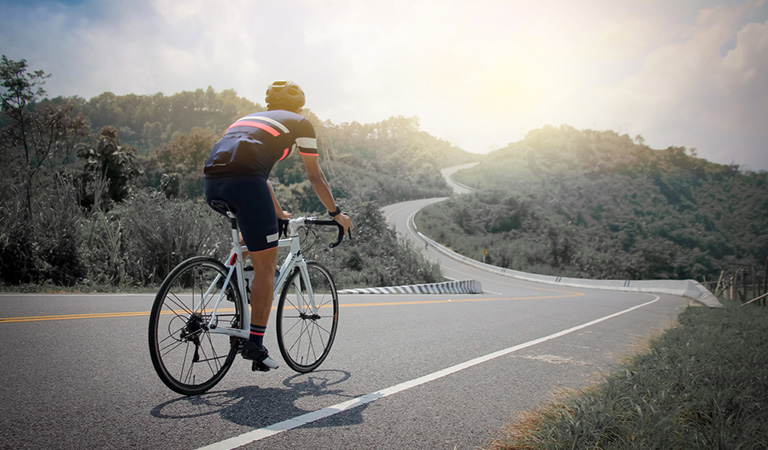

Choose a Good Road Bike:
Picking the right bike is essential for anyone who wants to take up cycling either as a profession or for leisure. Racing bikes are different from the normal bikes and come with different specifications; the same holds true for specialty bikes for people with physical and health challenges. Choosing the wrong bike may lead to future physical complications. Enlisting the help of an expert may help you in making the right choice as experience sometimes is important in making the right choice when faced with many alternatives.
Adjust the Road Bike Properly:
Having the right bike is not enough; you also need to adjust it to fit your personal needs. You will need to adjust the different components like:
- Saddle height: Wider saddles are advisable especially for recreational riders. The saddle height should be properly positioned to ensure proper elbow and waist symmetry. This will enable proper bending when reaching out for the handlebar.
- Saddle angle: Saddles should not be tilted forward as this will create pressure on the lower back. Improper angle placement may create tensions and cause numbness in the waist and bottom region.
- Forward/Backward Position: Frequently changing positions when cycling is very important. Forward and backward shifts at regular intervals increase blood flow and aids muscle movement.
- Handle Bar position: Adjust the handlebar to suit your frame before cycling. The bar should be positioned to allow space for the elbow to bend comfortably.

Select the Frame Geometry:
Select the proper bike frame which suits your physical frame and reach. In terms of stability, suitability, and comfort, the right frame geometry is important. Bike geometry preserves body angles while riding with the use of drop bars and bike frames unlike other components cannot be adjusted, so acquiring the proper frame geometry is very essential. Here are a few helpful tips to consider in selecting the perfect geometry;
- Buy a frame that fits: Concentrate on the right technology which maintains bike traction during motion. Focusing on the technology is not enough; you also need to ensure you get the frame measurement right in relation to your size. To get the right measurement;
- Be purpose specific: Bikes are of different kinds with specific purposes. Road bikes have different specifications specifically for cycling on roads. You need to make sure you are purchasing the right type of bike for your need.
- Take appropriate measurements: You need to take the appropriate measurement to avoid buying the wrong bike size – one of the common mistakes made by beginners. Measurements to consider are;
a) Limb measurement: Take your measurement by measuring in centimeters from your foot up to your waist or where your bike seat should be while standing.
b) Seatpost measurement: To get the appropriate seatpost measurement, multiply your limb measurement in centimeters by .67 to get the correct seat tube length.
- Adjust Seat Length before you test the bike frame: Seats can be adjusted to suit the rider so before you place your feet on the pedal ensure you adjust the seat slightly bent forward or in any comfortable angle for you. While pedaling, your knee should be slightly bent even when the pedal is on ground level.
- Find a frame whose reach you are comfortable with: The Frame geometry may be the right fit with adequate traction but if you still feel uncomfortable on it then it is not the right frame for you. Great care and attention is needed in picking the right frame. If you are not convinced then try a new frame until you find the right one.

Discuss about Your Pedaling Technique with a Specialist:
Seeking specialist advice on the proper pedaling technique is another sure way to go. Sport science specialists have the requisite skill and knowledge in dishing out sound and professional advice as regards the best pedaling technique for your individual fit. Consult a qualified specialist to help you identify the right technique for your physical frame. Other important issues like proper posturing can also be identified by the specialist.
Use Shock Absorbing Bike Accessories:
Useful bike accessories like shock absorbers help decrease the impact of jarring on the spine and pelvis when cycling in rough terrains. Cyclists who ride on rocky and rough terrains often complain about chronic back pain after cycling through rough countries. Shock absorbers help mitigate the impact of jarring which adversely affects the cyclist.

Two questions we have been able to answer in this article are “Is cycling good for lower back pain” and “Are road bikes bad for your back?” Cycling can be a curative measure for sufferers of back pains and road bikes are not necessarily bad for your back. However, the wrong bike fit and posture can have harmful effects on our back. Maintaining proper posture and pedaling techniques can prevent spinal and muscular problems. Understanding the difference between different bike types is also essential.